IBAN FAQ
Everything you need to know about International Bank Account Numbers
What is an IBAN?
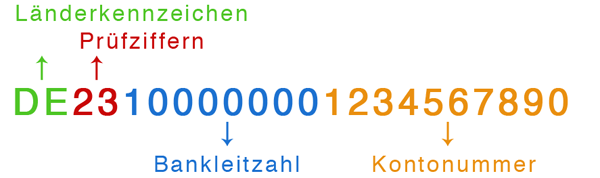
IBAN stands for "International Bank Account Number" and uniquely identifies a bank account. Since February 1, 2016, it has been mandatory for payments within Germany and the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA).
Before IBAN
Previously, bank transfers required separate account numbers and bank sort codes (BLZ). This system varied by country, causing confusion and errors in international transfers.
Old System in Germany:
- Account number: Varied in length (up to 10 digits)
- Bank sort code (BLZ): Always 8 digits
- No integrated error checking
- International transfers required additional information
Example of a typical bank code and account number combination
History and Introduction of IBAN
IBAN format established through the International Standard ISO 13616.
EU Regulation 2560/2001 laid the groundwork for introducing IBAN in Europe.
Beginning of the SEPA initiative (Single Euro Payments Area) to unify payment transactions.
IBAN becomes mandatory for transfers in Germany.
Complete transition: IBAN becomes obligatory for all payments in the SEPA region.
Over 77 countries worldwide use the IBAN system for standardized bank transactions.
SEPA Region
The SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) includes all EU countries plus Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, Monaco, San Marino, Andorra, Vatican City, and the United Kingdom. In this economic area, payments in euros are processed under uniform conditions using standardized instruments (IBAN, BIC).
Benefits of IBAN
IBANs offer a decisive advantage over traditional account numbers: they include a check digit that can detect input errors and number transpositions during entry, allowing them to be corrected immediately.
Enhanced Security
Check digit validation reduces problems caused by incorrect account numbers
Common errors like transposed numbers are immediately detected and cannot be processed
Faster Transfers
IBAN and BIC accelerate fund transfers via SEPA
Automated processing leads to shorter processing times, often within one business day
Standardization
Global standard for payment orders across countries
Simplifies international financial transactions through a uniform format in all participating countries
Error Prevention
Validates bank information before transfer
Significantly reduces returned payments and costs associated with failed transfers
Benefits for Different User Groups:
For Individuals
- Simplified international shopping
- Faster refunds
- Fewer payment errors
For Businesses
- More efficient invoicing
- Improved cash flow planning
- Simplified cross-border payments
For Banks
- Reduced error rates
- Standardized processes
- Cost savings through automation
IBAN in Practice
How is IBAN Used?
The IBAN is now a central component of payment transactions and is used in the following situations:
- For transfers and direct debits within the SEPA region
- Setting up standing orders
- Providing bank details for payroll processing
- Online payments and shopping
- International money transfers (often together with BIC)
Important Security Note
Although IBAN is more secure than previous systems, you should only share your IBAN with trusted recipients. No unauthorized debits can be made with the IBAN alone, but combined with other data, fraudsters might attempt to set up unauthorized direct debits.
Learn More About IBAN
Learn more about how IBANs are structured or use our free IBAN Calculator to calculate or verify an IBAN.
Ready to Get Started?
Use IBANTEST for precise IBAN validation and calculation – reliable and user-friendly.