IBAN FAQ
Everything you need to know about International Bank Account Numbers
What is the BIC?
BIC stands for "Bank Identifier Code" and serves as a global identifier for financial institutions. It's an 8 or 11 character code that uniquely identifies a bank worldwide.
History and Purpose of BIC
The BIC was developed by the SWIFT network in the 1970s to uniquely identify banks worldwide and simplify international payment transactions. Prior to the introduction of international standards like BIC and IBAN, cross-border payments were complicated as each country used its own identifiers and formats.
The main purposes of the BIC are:
- Unique Identification: Each bank worldwide receives a unique code
- Message Routing: Used in the SWIFT network for precise transmission of messages between financial institutions
- Acceleration of Payment Transactions: Standardization enables automated processing
- Error Prevention: Minimization of confusion between similarly named banks in different countries
Key Facts About BIC
International Standard
Based on ISO 9362 for global standardization
Length Variations
Can be 8 characters (main branch) or 11 characters (specific branch)
SEPA Payments
Not required for domestic German payments - IBAN is sufficient
International Transfers
Required for transfers outside SEPA area or to certain countries
Structure of the BIC
Let's examine the structure using the BIC of the Deutsche Bundesbank in Berlin: MARKDEF1100
| Component | Length | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Code | 4 characters | MARK |
Freely chosen by the bank |
| Country Code | 2 characters | DE |
ISO 3166-1 country code |
| Location Code | 2 characters | F1 |
Location within the country |
| Branch Code | 3 characters (optional) | 100 |
Optional branch identifier |
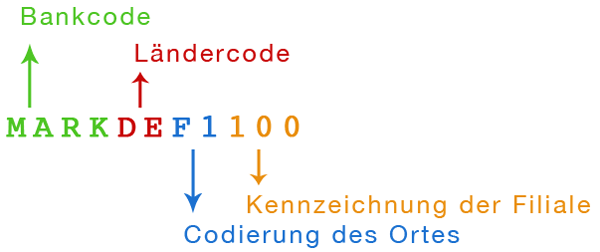
Visual representation of a BIC's structure
Frequently Asked Questions About BIC
Relationship Between BIC and IBAN
BIC and IBAN are different but complementary codes in international payment transactions:
BIC identifies the bank
The BIC indicates which bank is involved in the transaction and how the payment should be routed through the SWIFT network.
IBAN identifies the account
The IBAN specifies the individual bank account to which the payment should be sent or from which it should be debited.
For SEPA transfers within the EU, only the IBAN is required, as the system can determine the associated bank from the bank code contained in the IBAN. However, for international transfers outside the SEPA area, both BIC and IBAN are needed.
Find a BIC
Need to find the BIC for a specific bank? Use our free BIC Search Tool to look up BICs by bank name or IBAN.
Our tool offers the following advantages:
- Easy search by bank name, bank code, or IBAN
- Comprehensive database of German and international banks
- Immediate results without registration
- Free to use
Ready to Get Started?
Use IBANTEST for precise IBAN validation and calculation – reliable and user-friendly.